If you want to install a bunch of MSI files you put them in a folder and install them with a batch file. There is a downsize: you must modify the batch file for each situation. With this PowerShell script you can install all the MSI files in the folder, including applying transform and patch files. You can add your own properties in a csv settings file.
There are some parameters:
- Install:
Use this swith to specify an installation. - Uninstall:
Use this swith to specify an uninstall. - MSIPath:
Specify the location where the MSI files are located. - Loglocation:
Specify the logfile location. The default log location is C:\Windows\system32\LogFiles. - Silent
Silent parameter, like /qb! or /qn.
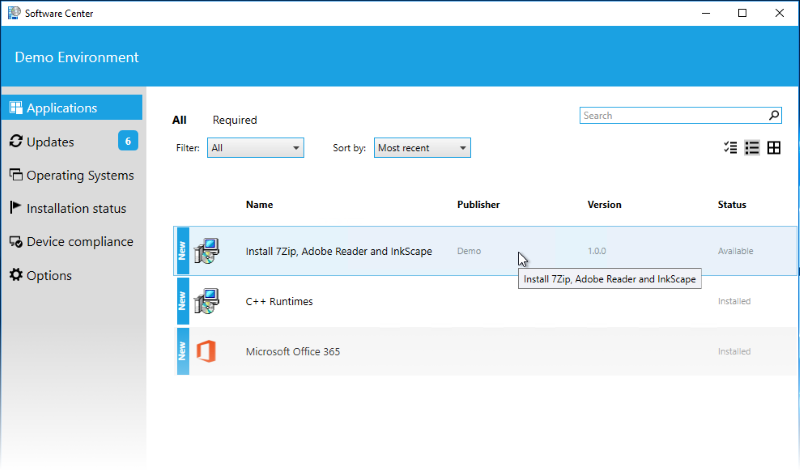
You can also use SCCM to install all the MSI files in the folder. Create an application with one deployment type. You can add all the product codes from each MSI file to identify a successful installation.
The Install line is:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -executionpolicy bypass -file "install_all_msi (v12).ps1"The Uninstall line is:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -executionpolicy bypass -file "install_all_msi (v12).ps1" -Uninstall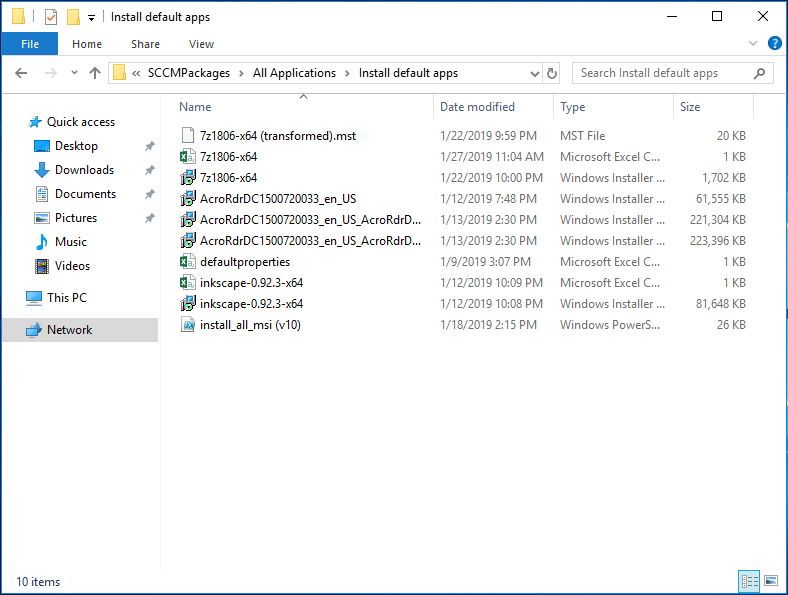







A demonstration of this script can be found on my YouTube channel: the script and AppV Repository or view it below:
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Installs all MSI's in a folder. By default, it is the folder where the script is located, but you can specify another location.
.DESCRIPTION
Installs all MSI's in a folder. By default, it is the folder where the script is located, but you can specify another location.
If there is a MST that starts with the MSI name, then the MSI / MST combination will be installed.
If there is a MSP that starts with the MSI name, then the MSI / MSP combination will be installed.
Valid combinations:
-> MSI file: Application_1.20.msi
-> MST file: Application_1.20_transform.mst
-> MSP file: Application_1.20_Update_to_1.40.msp
-> CSV file: Application_1.20.csv
Invalid combinations:
-> MSI file: Application_1.20.msi
-> MST file: Application_1.20.msi.mst (.msi should be removed)
-> MST file: Application_patch.msp (not the full msi file name)
.EXAMPLE
Installs all the MSIs that are in the folder where the script is located.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1"
.EXAMPLE
Installs all the MSIs that are in the folder where the script is located.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Install
.EXAMPLE
Installs all the MSIs that are in the folder where the script is located and run the cmd finalconfig.cmd afterwards.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Install -RunScriptAfter finalconfig.cmd
.EXAMPLE
Installs all the MSIs that are in the folder where the script is located and run the cmd beforeconfig.cmd before the install starts.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Install -RunScriptBefore beforeconfig.cmd
.EXAMPLE
Installs all the MSIs that are in the folder where the script is located and run the cmd beforeconfig.cmd before the install starts.
Include all the MST files that belongs to the specified application.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Install -RunScriptBefore beforeconfig.cmd -AllMSTFiles
.EXAMPLE
Uninstalls all the MSIs that are in the folder \\server\share\MSIs.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Uninstall -MSIPath \\server\share\MSIs
.EXAMPLE
Uninstalls all the MSIs that are in the folder \\server\share\MSIs and its sub folders. Logfiles are written to C:\Logs
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Uninstall -MSIPath \\server\share\MSIs -LogLocation C:\Logs -IncludeSubFolders
.EXAMPLE
Uninstalls all the MSIs that are in the folder \\server\share\MSIs and its sub folders. Logfiles are written to C:\Logs
Run the script before.cmd before the uninstall starts.
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Uninstall -MSIPath \\server\share\MSIs -LogLocation C:\Logs -IncludeSubFolders -RunScriptBefore before.cmd
.EXAMPLE
Uninstalls all the MSIs that are in the folder \\server\share\MSIs and its sub folders without any user interface. Logfiles are written to C:\Logs
."\install_all_msi (v16).ps1" -Uninstall -MSIPath \\server\share\MSIs -LogLocation C:\Logs -Silent /qn -IncludeSubFolders
.NOTES
Author: Willem-Jan Vroom
Website: https://www.vroom.cc/
Twitter: @TheStingPilot
v0.1:
* Initial version.
v1.0:
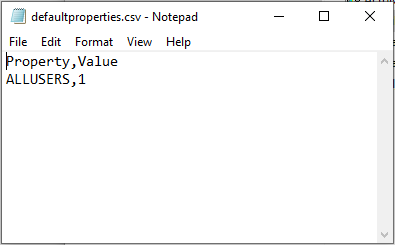
* Added: properties handler:
- defaultproperties.csv -> will be applied to all MSI packages or MSI / MST combination in the folder.
This file can be in either the location where the script is, or in the location
where the MSI files are.
- <name_of_msi>.csv -> will be applied only to the given MSI or MSI / MST combination.
This file must be in the same directory as the MSIs.
This file must have the following header layout:
Property,Value
ALLUSERS,1
ADDLOCAL,ALL
The content may be different.
* Install and uninstall switch added.
* Check if user has admin rights. It throws up an error in case not.
* Added the command line options MSIPath and LogLocation.
* Added patch support. The path name must start with have the same name as the MSI.
* Check if both install and uninstall switches are used.
* Bugfix: error messages when there are quotes around the MSI file name.
v1.1
* Some code improvements
v1.2
* Silent property can be added as a parameter
v1.3:
* Recursive search to MSI files.
v1.4:
* Implemented -RunScriptAfterBefore and -RunScriptAfter
* Implemented -AllMSTFiles
v1.5:
* Also reads the properties from a .msp file if needed.
* Introduced the command line option SuppressProgressBar
v1.6:
* The function Get-AllFilesWithPattern has been modified. If the MSI file was more than 1 level deep, the MSI
file was not found.
#>
[CmdLetBinding()]
param
(
# Use this switch to specify an installation.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[Switch] $Install,
# Use this switch to specify an uninstall.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[Switch] $Uninstall,
# Use this switch to specify a recursive search to MSI files.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[Switch] $IncludeSubFolders,
# Use this switch to specify that all MST files should be applied.
# By default only the last transform file is applied.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[Switch] $AllMSTFiles,
# Use this switch to suppress the progress bar that is shown during
# the installation.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[Switch] $SuppressProgressBar,
# Specify the location where the MSI files are located.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[String] $MSIPath = "",
# Specify the silent parameter, like /qb or /qn. Default = /qb!
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[String] $Silent = "/qb!",
# Specify the logfile location.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[String] $LogLocation = "",
# Specify the script to run before the installation or uninstall.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[String] $RunScriptBefore = "",
# Specify the script to run after the installation or uninstall.
[Parameter(Mandatory=$False)]
[String] $RunScriptAfter = ""
)
# ========================================================================================================================
# Function block
# ========================================================================================================================
Function CreateLogFile
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 9-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: CreateLogFile
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function creates the logfile
#>
param
(
[string] $LogFile
)
New-Item $LogFile -Force -ItemType File | Out-Null
}
Function WriteToLog
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 9-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: WriteToLog
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function adds a line to the logfile
#>
param
(
[string] $LogFile,
[string] $line
)
$timeStamp = (Get-Date).ToString('G').Replace("/","-")
$line = $timeStamp + " - " + $line
Add-Content -Path $LogFile -Value $line -Force
}
Function UserDetails
{
<#
.NOTES
=============================================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 03-Jan-21
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Functionname: UserDetails
=============================================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function returns 4 details of the Current Logged In Usser
1. The username of the current logged in user
2. User\Domain of the current logged in user
3. User SID fo the User\Domain
4. Account name that is using the script
#>
$UserName = Invoke-CimMethod -InputObject $(Get-CimInstance Win32_Process -Filter "Name = 'explorer.exe'") -MethodName GetOwner
$UserAndDomain = "$($Username.Domain)\$($Username.User)"
$SID = (Invoke-CimMethod -InputObject $(Get-CimInstance Win32_Process -Filter "Name = 'explorer.exe'") -MethodName GetOwnerSid).SID
$ScriptAccount = [System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent().Name
Return $($Username.User),$UserAndDomain,$SID,$ScriptAccount
}
Function Import-PropertyFile
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 9-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Import-PropertyFile
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function imports all the properties that are mentioned in the given property-file
#>
param
(
[string] $PropertyFile
)
$arrItems = @()
$strProperties = ""
if(Test-Path $PropertyFile)
{
$arrItems = @(Import-CSV $PropertyFile)
if($arrItems.Count -ge 1)
{
WriteToLog -LogFile $strLogFile -line "The property file '$PropertyFile' has been found and is applied."
ForEach($objItem in $arrItems)
{
$strProperty = $objItem.Property
$strValue = $objItem.Value
$strLine = $strProperty + "=" + $strValue + " "
$strProperties += $strLine
}
}
}
Return $strProperties
}
Function Get-MSIFileInformation
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 9-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Get-MSIFileInformation
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function reads the various properties from a MSI file.
This function has been found on http://www.scconfigmgr.com/2014/08/22/how-to-get-msi-file-information-with-powershell/
All credits, including the copyright go to Nickolaj Andersen.
#>
param
(
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[System.IO.FileInfo]$Path,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[ValidateSet("ProductCode", "ProductVersion", "ProductName", "Manufacturer", "ProductLanguage", "FullVersion")]
[string]$Property
)
Process
{
try
{
# Read property from MSI database
$WindowsInstaller = New-Object -ComObject WindowsInstaller.Installer
$MSIDatabase = $WindowsInstaller.GetType().InvokeMember("OpenDatabase", "InvokeMethod", $null, $WindowsInstaller, @($Path.FullName, 0))
$Query = "SELECT Value FROM Property WHERE Property = '$($Property)'"
$View = $MSIDatabase.GetType().InvokeMember("OpenView", "InvokeMethod", $null, $MSIDatabase, ($Query))
$View.GetType().InvokeMember("Execute", "InvokeMethod", $null, $View, $null)
$Record = $View.GetType().InvokeMember("Fetch", "InvokeMethod", $null, $View, $null)
$Value = $Record.GetType().InvokeMember("StringData", "GetProperty", $null, $Record, 1)
# Commit database and close view
$MSIDatabase.GetType().InvokeMember("Commit", "InvokeMethod", $null, $MSIDatabase, $null)
$View.GetType().InvokeMember("Close", "InvokeMethod", $null, $View, $null)
$MSIDatabase = $null
$View = $null
$ReturnValue = $($Value.ToString().Trim())
# Return the value
return $ReturnValue
}
catch
{
Write-Warning -Message $_.Exception.Message ; break
}
}
End
{
# Run garbage collection and release ComObject
[System.Runtime.Interopservices.Marshal]::ReleaseComObject($WindowsInstaller) | Out-Null
[System.GC]::Collect()
}
}
Function Get-MSPProperties
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 17-July-2020
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Get-MSPProperties
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function reads the various properties from a MSP file.
#>
param
(
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[String]$MSPPath,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[ValidateSet("UpdatedVersion","UpgradeCode","TargetProductCode","TargetVersion")]
[string]$Property
)
$WindowsInstaller = New-Object -ComObject WindowsInstaller.Installer
[xml]$MSPData = $WindowsInstaller.ExtractPatchXMLData($MSPPath)
Switch($Property)
{
"UpdatedVersion" {Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.UpdatedVersion)
Break
}
"UpgradeCode" {if(($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.UpGradeCode).Count -gt 0)
{
Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.UpGradeCode[0].'#text')
}
Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.UpGradeCode.'#text')
Break
}
"TargetVersion" {if(($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.TargetVersion).Count -gt 0)
{
Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.TargetVersion[0].'#text')
}
Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.TargetVersion.'#text')
Break
}
"TargetProductCode" {Return @($MSPData.MsiPatch.TargetProduct.TargetProductCode.'#text')
Break
}
}
}
Function Check-HasAdminRights
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 11-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Check-HasAdminRights
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function checks if an user has admin rights. The function returns $true or $false
#>
If (([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole] "Administrator"))
{
Return $True
}
else
{
Return $False
}
}
Function Remove-TrailingCharacter
{
<#
.NOTES
=============================================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 18-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Remove-TrailingCharacter
=============================================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function removes a trailing character from a string
#>
param
(
[string] $RemoveCharacterFrom = "",
[string] $Character = ""
)
if($RemoveCharacterFrom.Length -gt 0)
{
if(($RemoveCharacterFrom.SubString($RemoveCharacterFrom.Length-1,1)) -eq $Character)
{
$RemoveCharacterFrom = $RemoveCharacterFrom.Substring(0,$RemoveCharacterFrom.Length-1)
}
}
Return $RemoveCharacterFrom
}
Function Add-TrailingCharacter
{
<#
.NOTES
=============================================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 06-September-2018
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Add-TrailingCharacter
=============================================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function adds a trailing backslash to a string
#>
param
(
[string] $AddCharacterTo = "",
[string] $Character = ""
)
if($AddCharacterTo.Length -gt 0)
{
$AddCharacterTo = Remove-TrailingCharacter -RemoveCharacterFrom $AddCharacterTo -Character $([char]34)
if(($AddCharacterTo.SubString($AddCharacterTo.Length-1,1)) -ne $Character)
{
$AddCharacterTo = $AddCharacterTo + $Character
}
}
Else
{
$AddCharacterTo = $Character
}
Return $AddCharacterTo
}
Function Get-AllFilesWithPattern
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 13-January-2019 / Modified 12-February-2021.
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Get-AllFilesWithPattern
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
Find all files in the given folder that matches a filter.
#>
param
(
[string] $FolderToLookIn,
[string] $Pattern
)
$FolderToLookIn = Remove-TrailingCharacter -Character "\" -RemoveCharacterFrom $FolderToLookIn
$arrItems = @()
if ($IncludeSubFolders)
{
$arrItems = Get-ChildItem -Path $FolderToLookIn -Filter $Pattern | Sort-Object -Property FullName
}
else
{
$arrItems = Get-ChildItem -Path $FolderToLookIn -Filter $Pattern -Recurse -Depth 10 | Sort-Object -Property FullName
}
Return $arrItems
}
Function Get-LastItemOfAnArryAndPutItInAString
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 13-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Get-LastItemOfAnArryAndPutItInAString
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
Returns the last item of string.
#>
param
(
[string] $FileName,
[string] $OldExtension,
[string] $NewExtension,
[string] $WhereToLook
)
$arrFiles = @()
$strFileName = ""
$FilePattern = $FileName -Replace($OldExtension,$NewExtension)
$arrFiles = Get-AllFilesWithPattern -FolderToLookIn $WhereToLook -Pattern $FilePattern
if($arrFiles.Count -gt 0)
{
$strFileName = $arrFiles[-1].ToString()
}
Return $strFileName
}
Function Get-AllTranformFilesAndPutItInAString
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 13-January-2019
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: Get-AllTranformFilesAndPutItInAString
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
Returns all the transform files.
#>
param
(
[string] $FileName,
[string] $OldExtension,
[string] $NewExtension,
[string] $WhereToLook
)
$arrFiles = @()
$strFileName = ""
$FilePattern = $FileName -Replace($OldExtension,$NewExtension)
$arrFiles = Get-AllFilesWithPattern -FolderToLookIn $WhereToLook -Pattern $FilePattern
if($arrFiles.Count -gt 0)
{
ForEach ($FileName in $arrFiles)
{
if($strFileName -eq "")
{
$strFileName = $FileName
}
else
{
$strFileName = $strFileName + ";" + $FileName
}
}
}
Return $strFileName
}
Function InstalledVersion
{
<#
.NOTES
========================================================================================================================
Created with: Windows PowerShell ISE
Created on: 17-July-2020
Created by: Willem-Jan Vroom
Organization:
Functionname: InstalledVersion
========================================================================================================================
.SYNOPSIS
This function finds the installed version of a given productcode.
#>
param
(
[string] $ProductCodeToCheck
)
$DisplayVersion = ""
$ProductCodeToCheck = $ProductCodeToCheck.trim()
$X64 = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\$ProductCodeToCheck"
$X86 = $X64.Replace("WOW6432Node\","")
if(test-path $X64)
{
$DisplayVersion = (Get-ItemProperty -Path $X64 -Name "DisplayVersion").DisplayVersion
}
if(test-path $X86)
{
$DisplayVersion = (Get-ItemProperty -Path $X86 -Name "DisplayVersion").DisplayVersion
}
Return $($DisplayVersion.ToString().Trim())
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# End function block
# ========================================================================================================================
# ========================================================================================================================
# Define the variables.
# ========================================================================================================================
$strCurrentDir = Split-Path -parent $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Definition
if($MSIPath.Length -eq 0)
{
$MSIPath = $strCurrentDir
}
if($LogLocation.Length -eq 0)
{
$LogLocation = $Env:Windir + "\SYSTEM32\LogFiles"
}
$LogLocation = Add-TrailingCharacter -AddCharacterTo $LogLocation -Character "\"
$MSIPath = Add-TrailingCharacter -AddCharacterTo $MSIPath -Character "\"
$strCurrentDir = Add-TrailingCharacter -AddCharacterTo $strCurrentDir -Character "\"
$ComputerName = $env:COMPUTERNAME
$OnlyUserName,$LoggedOnUserInDomainFormat,$UseridSID,$InstallAccount = UserDetails
$strTransform = ""
$strDefaultPropFile = $MSIPath + "defaultproperties.csv"
$strDefaultProperties = ""
$strActivity = ""
$strPatch = ""
$strSingleOrMultipleMSI = "MultipleMSI"
$arrDefaultProperties = @()
$arrMSPFiles = @()
$arrMSIFiles = @(Get-AllFilesWithPattern -FolderToLookIn $MSIPath -Pattern "*.msi")
$numMSIFiles = $arrMSIFiles.Count
$numCounter = 1
# ========================================================================================================================
# Stop the script for a non admin user
# ========================================================================================================================
if(-not(Check-HasAdminRights))
{
Write-Error "The current user has no admin rights. Please rerun the script with elevated rights." -Category PermissionDenied
Exit 999
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Create the log file location if not exists
# ========================================================================================================================
if(-not (Test-Path $LogLocation))
{
New-Item -Path $LogLocation -ItemType Directory -Force -Confirm:$False | Out-Null
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Define the logfile for the install or uninstall of all the MSIs.
# ========================================================================================================================
$strLastPartOfFileName = " (" + (Get-Date).ToString('G') + ").log"
$strLastPartOfFileName = $strLastPartOfFileName.Replace(":","-").Replace("/","-")
if($numMSIFiles -eq 1)
{
$strSingleOrMultipleMSI = "SingleMSI"
}
if($Install -or (-not $Uninstall))
{
$strLogFile = $LogLocation + $strSingleOrMultipleMSI + $strLastPartOfFileName
$strActivity = "Installing MSIs in the folder $MSIPath"
}
else
{
$strLogFile = $LogLocation + "Uninstall" + $strSingleOrMultipleMSI + $strLastPartOfFileName
$strActivity = "Uninstalling MSIs in the folder $MSIPath"
}
CreateLogFile -LogFile $strLogFile
# ========================================================================================================================
# Give an error message if both parameters install and uninstall are used.
# ========================================================================================================================
if($Install -and $Uninstall)
{
$strErrorMessage = "Both install and uninstall parameters are mentioned. That is not possible. Only one of them should be used."
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "FATAL ERROR!" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line $strErrorMessage -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
Write-Error $strErrorMessage -Category InvalidArgument
Exit 991
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Write default settings to the logfile
# ========================================================================================================================
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "Log location: $LogLocation" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "MSI Path: $MSIPath" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "Logged in user: $LoggedOnUserInDomainFormat" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "Installation account: $InstallAccount" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "Computername $ComputerName" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "Silent parameter: $Silent" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line $($strActivity + ":") -LogFile $strLogFile
ForEach ($objMSIFile in $arrMSIFiles)
{
WriteToLog -line " * $($objMSIFile.Name) in $($objMSIFile.Directory)." -LogFile $strLogFile
}
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
# ========================================================================================================================
# In case of an installation:
# Define the default properties.
# ========================================================================================================================
if ($Install -or (-not $Uninstall))
{
$strDefaultProperties = Import-PropertyFile -PropertyFile $strDefaultPropFile
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Run a script before the install or uninstall starts.
# ========================================================================================================================
if($RunScriptBefore)
{
if(-not(Split-Path($RunScriptBefore)))
{
$RunScriptBefore = $strCurrentDir + $RunScriptBefore
}
if(Test-Path($RunScriptBefore))
{
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
$RunScriptBefore = $([char]34) + $RunScriptBefore + $([char]34)
WriteToLog -line "Running command: $RunScriptBefore" -LogFile $strLogFile
$StartProcess = (Start-Process -FilePath $RunScriptBefore -Wait -PassThru)
WriteToLog -line "Result: $($StartProcess.ExitCode)" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
else
{
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog "The script $RunScriptBefore does not exist."
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Start the real installation or uninstall.
# The installation is skipped if a MSI has already been installed.
# The uninstall is only done if the product has already been installed.
# ========================================================================================================================
ForEach ($objMSIFile in $arrMSIFiles)
{
$strMSIFileName = $($objMSIFile.Fullname)
$MSIPath = Add-TrailingCharacter -AddCharacterTo (Split-Path $strMSIFileName) -Character "\"
if (-not $SuppressProgressBar)
{
Write-Progress -Activity $($strActivity + ".") -Status "Processing '$objMSIFile' in '$MSIPath'." -PercentComplete ($numCounter / $numMSIFiles * 100)
}
$strMSPFileName = Get-LastItemOfAnArryAndPutItInAString -FileName $objMSIFile -OldExtension ".msi" -NewExtension "*.msp" -WhereToLook $MSIPath
$strProductName = Get-MSIFileInformation -Path $strMSIFileName -Property ProductName
$strProductVersion = Get-MSIFileInformation -Path $strMSIFileName -Property ProductVersion
$strProductCode = Get-MSIFileInformation -Path $strMSIFileName -Property ProductCode
$strProductVersion = $strProductVersion[-1].ToString()
$strProductName = $strProductName[-1].ToString()
$strProductCode = $strProductCode[-1].ToString()
if($strMSPFileName)
{
$strProductVersion = (Get-MSPProperties -MSPPath $($MSIPath+$strMSPFileName) -Property UpdatedVersion).ToString()
}
$strRegPathX64 = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\$strProductCode"
$strRegPathX64 = $strRegPathX64.Replace(" ","")
$strRegPathX86 = $strRegPathX64.Replace("WOW6432Node\","")
if($Install -or (-not $Uninstall))
{
# ========================================================================================================================
# The install
# ========================================================================================================================
$strTransform = ""
$strPatch = ""
if($AllMSTFiles)
{
$strMSTFileName = Get-AllTranformFilesAndPutItInAString -FileName $objMSIFile -OldExtension ".msi" -NewExtension "*.mst" -WhereToLook $MSIPath
}
else
{
$strMSTFileName = Get-LastItemOfAnArryAndPutItInAString -FileName $objMSIFile -OldExtension ".msi" -NewExtension "*.mst" -WhereToLook $MSIPath
}
$strPropFile = $strMSIFileName.Replace("msi","csv")
# ========================================================================================================================
# Apply a patch (msp file) (if available)
# ========================================================================================================================
$strPatchLogFile = ""
if($strMSPFileName)
{
$strPatch = " /update $([char]34)$MSIPath$strMSPFileName$([char]34)"
WriteToLog -LogFile $strLogFile -line "The patch file '$strMSPFileName' has been found and is applied."
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Apply a transform file (mst) (if available)
# ========================================================================================================================
if($strMSTFileName)
{
ForEach($objMSTFileName in ($strMstFileName -Split ";"))
{
WriteToLog -LogFile $strLogFile -line "The transform file '$objMSTFileName' has been found and is applied."
}
$strTransform = "TRANSFORMS=" + $([char]34) + $strMSTFileName +$([char]34) + " "
}
WriteToLog -line "Installing application: $strProductName" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "ProductVersion: $strProductVersion" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "ProductCode: $strProductCode" -LogFile $strLogFile
$InstalledVersionToCheck = InstalledVersion -ProductCodeToCheck $strProductCode
if($InstalledVersionToCheck)
{
WriteToLog -Line "Installed ProductVersion: $InstalledVersionToCheck" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
if((-not $InstalledVersionToCheck) -or ($InstalledVersionToCheck -lt $strProductVersion))
{
$strProperties = " "
$strProperties = Import-PropertyFile -PropertyFile $strPropFile
$strMSILogFile = "/l*v " + $([char]34) + $LogLocation + $strProductName + " " + $strProductVersion + $strPatchLogFile + ".log" + $([char]34)
$strArguments = "/i " + $([char]34) + $MSIPath + $objMSIFile + $([char]34) + $strPatch + " " + $Silent + " " + $strDefaultProperties + $strProperties + $strTransform + $strMSILogFile
$strArguments = $strArguments.Replace(" ","")
WriteToLog -line "Command that is run: msiexec $($strArguments)" -LogFile $strLogFile
$StartProcess = (Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList $strArguments -Wait -PassThru)
$MSIExitCode = $($StartProcess.ExitCode)
WriteToLog -line "Result: $MSIExitCode" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
else
{
if(-not $InstalledVersionToCheck)
{
WriteToLog -line "This application has already been installed, thus skipping." -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
else
{
WriteToLog -Line "The version $InstalledVersionToCheck has already been installed. No need to install the older version $strProductVersion." -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
}
}
else
{
# ========================================================================================================================
# The uninstall
# ========================================================================================================================
WriteToLog -line "Uninstalling application: $strProductName" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "ProductVersion: $strProductVersion" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "ProductCode: $strProductCode" -LogFile $strLogFile
if((Test-Path $strRegPathX64) -or (Test-Path $strRegPathX86))
{
$strMSILogFile = "/l*v " + $([char]34) + $LogLocation + "Uninstall_"+ $strProductName + " " + $strProductVersion +".log" + $([char]34)
$strArguments = "/x " + $strProductCode + " " + $Silent + " " + $strMSILogFile
$strArguments = $strArguments.Replace(" ","")
WriteToLog -line "Command that is run: msiexec $($strArguments)" -LogFile $strLogFile
$StartProcess = (Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList $strArguments -Wait -PassThru)
$MSIExitCode = $($StartProcess.ExitCode)
WriteToLog -line "Result: $MSIExitCode" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
else
{
WriteToLog -line "This application has not been installed, thus skipping." -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line " " -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
}
$numCounter++
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Run a script after the install or uninstall.
# ========================================================================================================================
if($RunScriptAfter)
{
if(-not(Split-Path($RunScriptAfter)))
{
$RunScriptAfter = $strCurrentDir + $RunScriptAfter
}
if(Test-Path($RunScriptAfter))
{
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
$RunScriptAfter = $([char]34) + $RunScriptAfter + $([char]34)
WriteToLog -line "Running command: $RunScriptAfter" -LogFile $strLogFile
$StartProcess = (Start-Process -FilePath $RunScriptAfter -Wait -PassThru)
WriteToLog -line "Result: $($StartProcess.ExitCode)" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
else
{
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
WriteToLog "The script $RunScriptAfter does not exist."
WriteToLog -line "========================================================================================================================" -LogFile $strLogFile
}
}
# ========================================================================================================================
# Done!
# ========================================================================================================================
WriteToLog -line "Exitcode: $MSIExitCode" -LogFile $strLogFile
Exit $MSIExitCode